The Global Business Complexity Index 2021 provides a panoramic overview of the complexity with which those who have or manage international activities are facing. The index classifies the 77 Countries, that are together responsible for 92% of the Worlds’ Gross National Product, based on 292 different indicators that describe the complexity in legal terms, compliance, accounting methods, fiscal terms and human resources management.
These countries have presented the following tendencies during the past year:
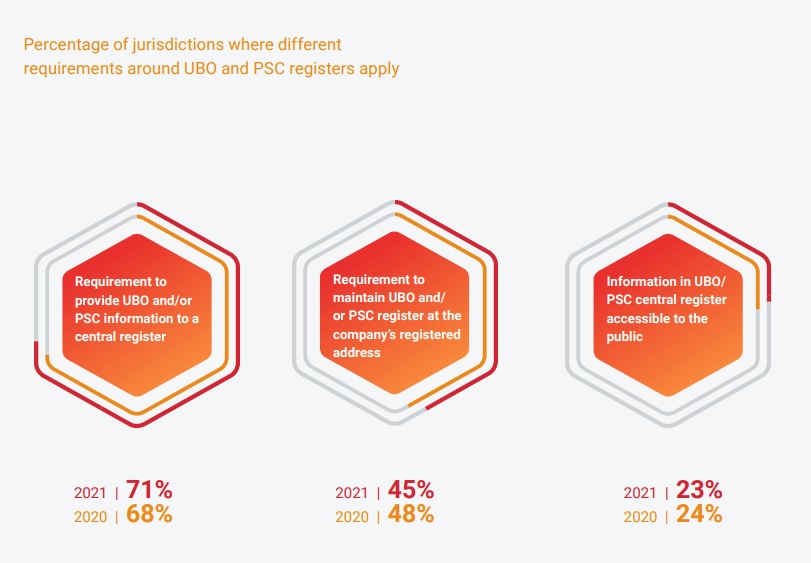
Increase in government responsibility, understood as a greater focus on acting in a more transparent way and socially responsible manner. Regarding transparency, the cornerstone of responsible governance, the index reveals how from 2020 the percentage of jurisdictions adopting ownership registers has remained stable, demonstrating the constancy of the trend. The necessity to provide information regarding UBOs (Ultimate Beneficial Owner) and PSCs (People with Significant Control) is particularly high in EMEA, where it is mandatory in 82% of jurisdictions compared to 43% in APAC. In addition, the trend of offshoring declined globally in 2021, with more companies encouraged to become tax law subjects of the countries in which they actually operate. The mandatory involvement of a third party in business operations has become more common, in 2020 only 17% of the analyzed jurisdictions have imposed it while in 2021, the percentage rose to 27%. A certified consultant/commercial advisor, according to the index, should in fact help reduce errors and failures in documentation, supporting companies and thus prompting them to act more responsibly. Further evidence of accountability growth in governance is the decrease of number of countries in which it is possible to fire an employee without a valid reason by a third, from 29% in 2020 to 20% in 2021.
The second tendency is the simplification across digitalization, a transformation which Covid has accelerated. In 2020 43% of jurisdictions didn’t consider electronic signatures valid, while today this only 38% of them don’t. 14% of them have adopted a system that digitally sends information to all state authorities, regarding the creation, closure or other variations seen in the life of a company. This year, an increase has been seen for: existence of online portals for the electronic transmission of fiscal documents (from 24% to 27%) and the frequency of sanctions for defaulted companies (93% of jurisdictions have a sanction in place, unlike 84% in 2020). The research shows a connection between complexity and a sanctioning law, I.e. the countries with stricter fiscal criteria and more complex norms are also the ones that undertake more drastic measures in confronting the companies that do no respect them. The most drastic measure, stripping the company of its license has been reported in 60% of the cases, while last year, it has been reported in only 45% of cases.
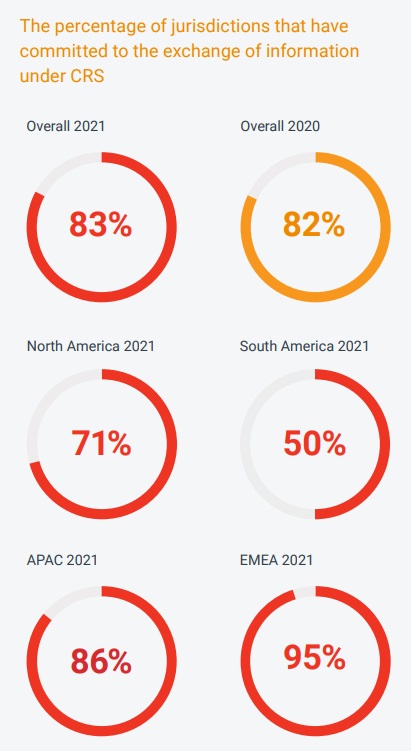
The third trend is the push for regulatory alignment between jurisdictions and the necessity to coincide with the local variations. The OECD's Common Reporting Standard (CRS) is one of the most recent examples of new international legislation aimed at regulating trade agreements between countries. Created to combat tax evasion, it mandates governments who are members to share companies' financial information according to common standards. Over the past year, the percentage of countries that have adopted it has risen slightly, from 82% to 83%. At the same time, individual jurisdictions are attempting to dismantle local regulations that appear to be in conflict with international agreements, although in some areas (tax above all) the former continue to prevail. In 57% of the analyzed countries it is mandatory for all companies to comply with national reporting requirements, but in only 19% of cases IFRS is mandatory. Local differences in regulation, however, represent a complexity for companies operating in multiple countries, and the overall trend is to try to minimize these differences.
Finally, the Global Business Complexity Index 2021 ranks the most complex jurisdictions for companies, based on the sum of the indicators considered. Following are the top ten. In order to see the full report please click here.